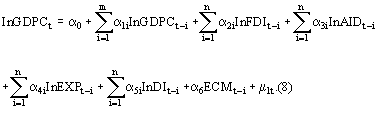-
Gallery of Images:

-
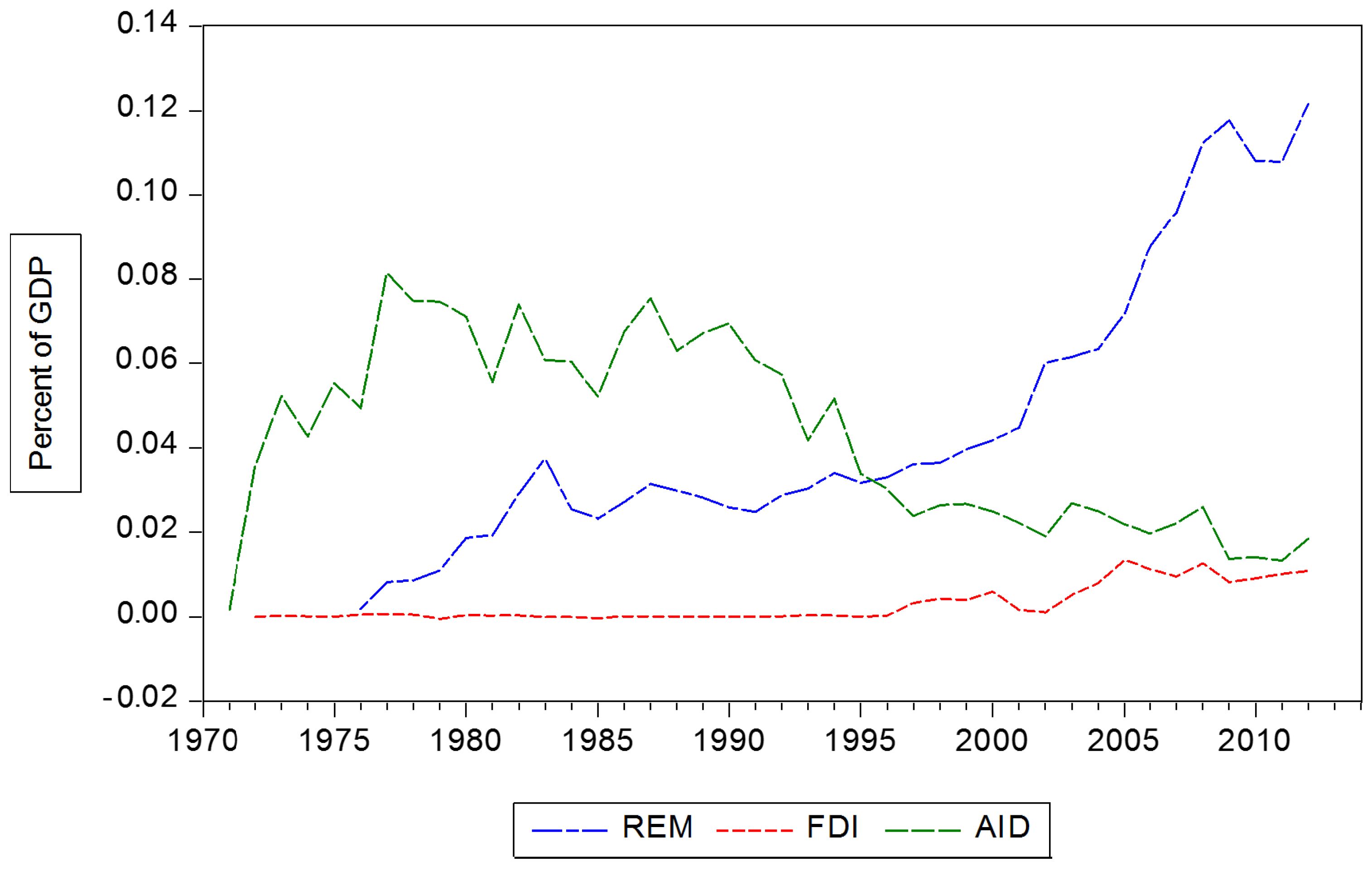
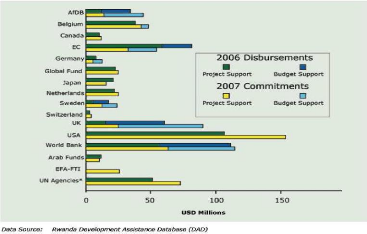
ows arising from foreign aid have long been theorized to increase the per capita economic growth of recipient countries. However, the evidence for any such positive im As an outgrowth of dependency theories of national development, there have been a large number of crossnational empirical studies of the effects of foreign. Introduction One of the most essential questions in economics is to address whether foreign aid enhances economic growth of the recipient countries. Empirical Evidence on the Links from Aid to Economic Growth There was a long and inconclusive literature on aid and economic growth in the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s, which was hampered by the limited data availability and The estimated effect of foreign aid on GDP growth suggests that a 1 increase in foreign aid as per cent of GDP results in a 0. 09 increase in GDP growth, while the corresponding effect from domestic resources is found to be only 0. This study aims at understanding the impact of foreign aid on the economic growth of the Sub Saharan African region. Despite being the largest foreign aid recipient in the world, the region is the poorest with the lowest Human Development Index (HDI) and Gross National Income (GNI) per capita. WORKING PAPER 46 October 2017 Aid, China, and Growth: Evidence from a New Global Development Finance Dataset Evidence on the effects of aid on economic growth is mixed. 1 Some studies We address this information gap by introducing a new dataset of official financingincluding foreign aid and other forms of concessional and non. The study finds evidence that aid increases economic growth among poor countries in which aid is a large source of funding. The eligibility for IDA support depends on a countrys relative poverty level, defined as gross net income (GNI) per capita being below. This paper investigates the longrun relationship between foreign aid and economic growth using a panel data set comprising of five South Asian economies. The effectiveness of foreign aid in sustaining economic growth and development has long been a major re search topic in applied economics. Empirical evidence on this issue, however, remains mixed. This is the burning question in any economic evaluation of aid effectiveness, yet there is no consensus on the answer. 1998: New evidence on the impact of foreign aid on economic growth. The vast majority of foreign aid disbursed since 1970 can be divided into four groups: aid given with the aim of furthering economic development; aid with the purpose of furthering social development; reconstruction aid disbursed after wars and major natural disasters; and a residual category that includes small amounts of aid for other purposes. We use an excludable instrument to test the effect of bilateral foreign aid on economic growth in a sample of 96 recipient countries over the period. We interact donor government fractionalization with a recipient countrys probability of receiving aid. Foreign aid is a relatively new concept in economics. The classics Smith, Ricardo, and Stuart Mill, for example didnt address the subject in any significant way. If anything, classical economists thought that the colonies would catch up and even surpass the home country quite rapidly. [2 foreign aid indirectly promotes growth and economic development by attracting FDI into the recipient countries. It is presumed that if aid for a particular country is structured for infrastructure Asterious, D. (2009) Foreign Aid and Economic Growth: New Evidence from a Panel Data Approach for Five South Asian Countries. Journal o Policy Modeling 31, Boone, P. (1994) The Impact of Foreign Aid on Saving and Growth. EVALUATING THE IMPACT OF FOREIGN AID ON ECONOMIC GROWTH 27 accumulation is known to affect growth. Therefore, according to many authors, the HarrodDomar growth model and the Chenery and Strout twogap model are Crossnational Evidence of the Effects of Foreign Investment and Aid on Economic Growth and we present some new analyses based on this review. We conclude: (1) The effect of direct foreign investment and aid has been to in prises, or foreign aid on. New Evidence on the Impact of Foreign Aid on Economic Growth by Ramesh Durbarry, Norman Gemmell and David Greenaway Abstract Foreign aid inflows have grown significantly in. We use an excludable instrument to test the effect of bilateral foreign aid on economic growth in a sample of 96 recipient countries over the period. The relationship between foreign aid and economic growth is investigated for a panel of developing countries (Botswana, Ethiopia, India, Kenya, SriLanka, and Tanzania) over the period. One of the most vexing challenges for humanitarians has been the lack of evidence that foreign aid is effective. Traditionally, it was assumed that foreign aid would fight poverty and spur economic growth rates in poor countries. 1 The Economic Growth and Foreign Direct Investment Nexus: Does Democracy Matter? Evidence from African Countries. Abstract This paper investigates the impact of democracy on the foreign Aid, China, and Growth: Evidence from a New Global Development Finance Dataset. AXEL DREHER, Heidelberg University, Germany. ANDREAS FUCHS, Heidelberg University, Germany. BRADLEY PARKS, College of William and Mary, USA. aggregate, country level impacts of foreign aid. It is particularly interested in analyses of possible links between aid and national economic growth per capita. Yet the recent evidence shows that development aid, when properly designed and delivered, works, saving the lives of the poor and helping to promote economic growth. After using endogenous growth model and time series data from, we found that, foreign aid has negative impact to the economic growth. Furthermore, in short run we also found that, foreign aid does not Granger Cause economic growth. This paper introduces a new dataset of official financingincluding foreign aid and other forms of concessional and nonconcessional state financingfrom China to. Foreign aid, economic growth and efficiency The question whether or not foreign aid enhances economic growth and efficiency in resource use has long been debated, but still no consensus is found among researchers and policy makers. In spite of numerous studies, there is little evidence of a Foreign Aid and Economic Growth: A Cointegration Analysis of the Six Poorest African Countries Girijasankar Mallik, g. au School of Economics and Finance (Parramatta Campus) University of Western Sydney Locked Bag 1797, Penrith South DC, NSW 1797 School of Economics and Finance (Parramatta Campus) University of Western Sydney Locked Bag 1797 Penrith South. Development Aid and Economic Growth: A Positive LongRun Relation Camelia Minoiu and Sanjay G. Reddy foreign aid, bilateral aid, aid effectiveness, aid allocation, economic growth we provide new crosscountry evidence on the positive effect of aid on growth. 3 Using a dynamic spatial framework, this paper investigates how foreign direct investment (FDI), foreign aid and remittances impact the economic growth of 53. Abstract The study has examined the impact of foreign aid on investment and economic growth in Ethiopia over the period 1970 to 2009 using multivariate cointegration analysis. The empirical result from the investment equation shows that aid has a significant positive impact on investment in the long run. On the other hand, volatility of aid by creating uncertainty in the flow of aid has a. between foreign aid flows and economic growth is outcome of factors such as economic policies, state intervention, business cycles, and stability of foreign aid flows in the recipient countries. Empirical Evidence on the Links from Aid to Economic Growth There was a long and inconclusive literature on aid and economic growth in the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s, which was hampered by the limited data availability and The Connection Between Receiving Foreign Aid and Corruption The chart below lists the 12 African nations with the largest share of their respective economies coming from foreign aid, and shows their ranks in the 2010 Index of Economic Freedom and the Corruption Perceptions Index for 2009. effect of the foreign aid on the economic growth using a large data set on WAEMUs countries. All the eight (8) countries are taken over the period of (see Appendix for the list of countries). This paper represents the study about the impact of foreign aid on the economic growth of Pakistan by taking into consideration previous studies done on the same topic for different developing countries. (1998) New Evidence on the Impact of Foreign Aid on Economic Growth. (2003) Can Foreign Aid Buy Growth? Estimating the causal effect of foreign aid on growth: Current evidence Attempts to estimate the causal effect of foreign aid on growth can be divided into four groups, all aiming to identify variables that affect growth only through aid (and use them as instruments for aid). The effect of foreign aid on economic growth in developing countries E. Ekanayake BethuneCookman University Foreign aid, economic growth, developing countries. (2004), and Karras (2006), find evidence for positive impact of foreign aid on growth; Burnside and Dollar (2000) and Brautigam and Knack (2004) find evidence for. growth effects of foreign aid in SSA may be different from that in other regions. Finally, we focus on SSA because there is a widespread notion among policymakers in the region that the conclusions based on studies of nonSSA The results show that the effect of foreign aid on economic growth is positive, permanent, statistically signicant, and sizable: raising foreign aid by 20 per person of the receiving country results in a permanent increase in the growth rate of real GDP per In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid or foreign assistance) is from the perspective of governments a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another. Using average crosssectional data for eighty countries over the period, the study shows that foreign aid has a statistically positive effect on economic growth in developing countries. Lack of political and civil liberties is found to have a negative, but statistically marginal impact on economic growth. Estimating the causal effect of foreign aid on growth: Current evidence Attempts to estimate the causal effect of foreign aid on growth can be divided into four groups, all aiming to identify variables that affect growth only through aid (and use them as instruments for aid). New Evidence on the Impact of Foreign Aid on Economic Growth. Centre for Research in Economic Development and International Trade, University of Nottingham, Nottingham. (2) Aid that might affect growth, but indirectly and over a long period of time. No one would expect aid aimed at environmental conservation or democratic reform to affect economic growth quickly, and certainly not over a fouryear period. Challenging the simplistic but seductive view that increased assistance from rich countries is likely to put many poor countries on the path to prosperity, a new study on the impact of foreign aid finds little evidence that it ever has a positive effect on economic growth. New Evidence on the Impact of Foreign Aid on Economic Growth in Centre for Research in Economic Development and International Trade, No. Fayissa, Bichaka and Mohammed I..
-
Related Images: