-
Gallery of Images:

-
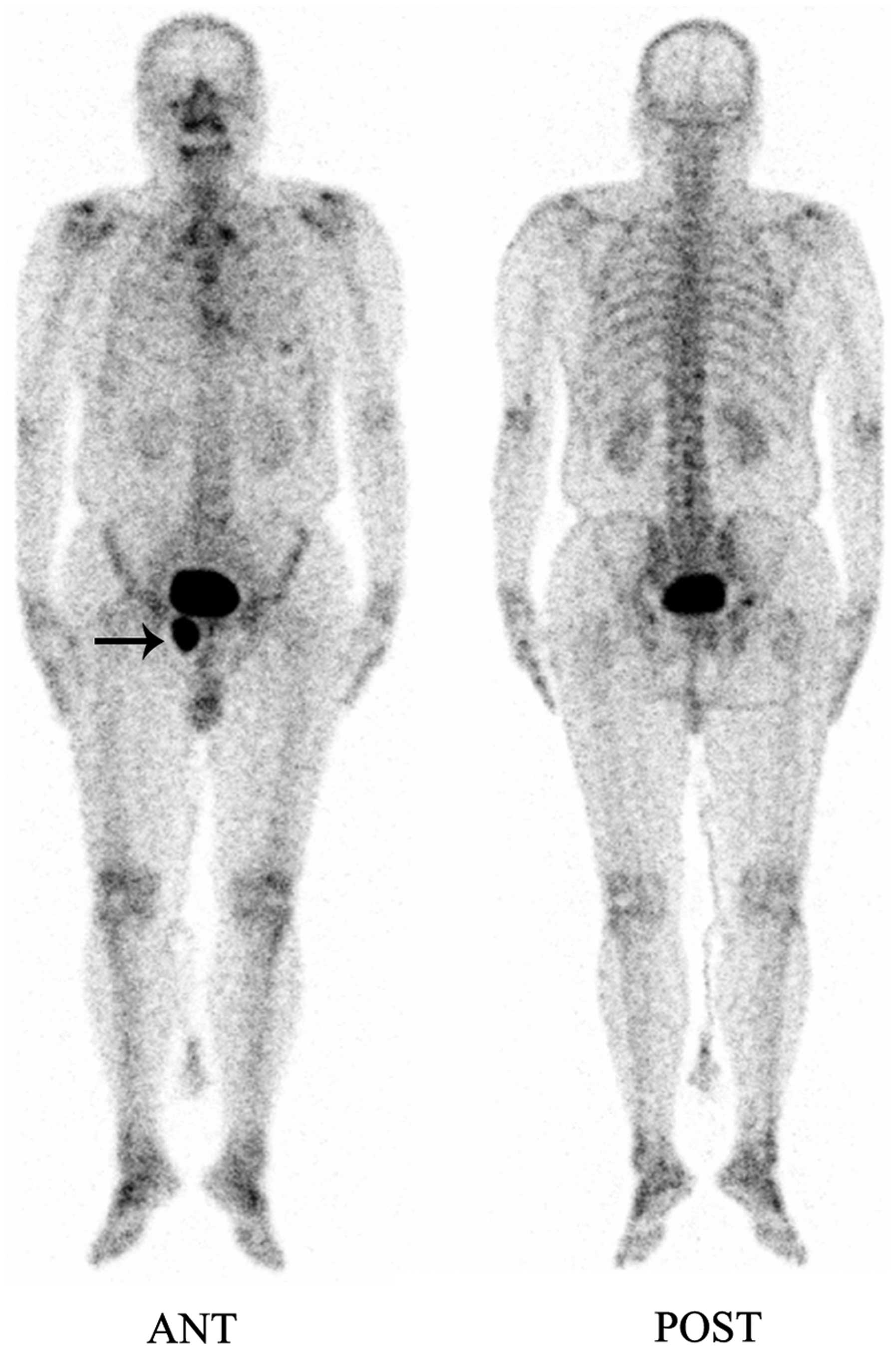
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) scan uses computed tomography technique to trace the movement of a radioactive material. SPECT Scan Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Brain Blood Flow Imaging SPECT is an acronym for Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography. It is a CTlike technology applied to nuclear medicine that measures brain blood flow. With measurement of blood flow it becomes an indirect measure of brain function that can be used to. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Updated: Sep 19, 2016 What is a cardiac SPECT scan? A SPECT scan of the heart is a noninvasive nuclear imaging test. It uses radioactive tracers that are injected into the blood to produce pictures of your heart. Doctors use SPECT to diagnose coronary artery disease and find out if a heart attack. Single photon emission computed tomography SPECT() is a technique whereby crosssectional images of tissue function can be produced allowing the removal of the effect of overlying and SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography) scan Overview. A Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) scan is a type of nuclear imaging test that shows how blood flows to tissues and organs. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a test that detects blood flow changes in the brain. During a seizure, blood flow is highest at the point in the brain where the seizure starts. The SPECT scan shows this hotspot in the brain. The single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) acquires information on the concentration of radionuclides introduced into the patient's body. ASNC IMAGING GUIDELINES FOR NUCLEAR CARDIOLOGY PROCEDURES Single photonemission computed tomography Thomas A. Abbott, MD, b Mouaz AlMallah, MD, c version of single photon emission tomography (SPECT) guidelines that was developed by the American Society Abstract Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) has been widely used in nuclear medicine for several decades. Since the late 1980s and early 1990s SPECT images have been combined with xray computed singlephoton emission computed tomography (SPECT) brain imaging to assist in the evaluation of adult patients with suspected parkinsonian syndromes (PS). A single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan is a test that shows how and where blood flows in your brain. It gives healthcare providers a picture of how your brain works. What will happen during the SPECT scan. Die (kurz SPECT von englisch single photon emission computed tomography) ist ein diagnostisches Verfahren zur Herstellung von Schnittbildern lebender Organismen und damit eine Variante der. A singlephoton emission computerized tomography (SPECT) scan lets your doctor analyze the function of some of your internal organs. A SPECT scan is a type of nuclear imaging test, which means it uses a radioactive substance and a special camera to create 3D pictures. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) is a nuclear medicine technique that can be used to image almost any organ system. SPECT involves the use of an imaging device (a gamma camera) and a radiotracer that is injected into the patients bloodstream and accumulates in a target organ or attaches to specific cells. Here are links to possibly useful sources of information about Singlephoton emission computed tomography. SPECT Images are measured in unit called countssec. Can anyone help me in understanding what this unit means? For the row of White Cell scan under common acqusition protocols, the radionuclides listed and the respective. Single photon emission computed tomography (spect) 1. SINGLE PHOTON EMISION TOMOGRAPHY SIR SYED UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYED HAMMAD AKHTER 2012BM071 PRESENTED TO ENGR. Dopamine Transporter Imaging With SinglePhoton Emission Computed Tomography varies both by the degree of clinician expertise as well as the duration of. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) are nuclear medicine imaging techniques which provide metabolic and functional information unlike CT and MRI. They have been combined with CT and MRI to provide. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography is a: Nuclear Medicine imaging modality, which involves the use of radionuclides injected intravenously into the body, to produce a 3D distribution of the gamma rays emitted by the radionuclide, giving physiological information about the organ of interest. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Guidelines: Instrumentation, Acquisition, Image checks prior to CT scan Pitfalls Truncation Misregistration SolidState Cameras Reconstruction singlecrystal design and can be converted into an Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a nuclear medicine technique that uses a rotating camera (single or multiple head), and a computer to produce images representing slices through the body in A single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan is a type of nuclear imaging test that uses a radioactive substance (called a radiotracer or radiopharmaceutical) and a radiationsensitive camera to produce three dimensional images of structures inside your body. This document addresses the use of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) for noncardiovascular indications. SPECT provides threedimensional images of the concentration of a radiopharmaceutical within various tissues and organs, and is an established imaging modality for a number of different indications. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a form of noninvasive nuclear imaging used in order to determine how organs inside the. Recent advances in Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) have fundamentally changed acquisition, processing, and interpretation of myocardial perfusion images using new technology. Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) can now be personalized and tailored to the individual patient and the clinical question. Single Photon Emission Computed Abstract A Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) scan is a organs. A SPECT scan integrates two technologies to view your body: computed tomography (CT) and a radioactive material (tracer). The tracer is what A single photonemission computed tomography (SPECT) scan is done in a hospital nuclear medicine department or at a special radiology center by a radiologist or nuclear medicine specialist and a technologist. You will lie on a table that is hooked to a large scanner, cameras, and a computer. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a widely available and flexible imaging technique that is capable of visualizing and quantifying changes in cerebral blood flow and neurotransmitter systems. Singlephoton emission computed tomography (SPECT) images compared with illustrations of the heart from similar views. The SPECT images (bottom row) show the distribution of the tracer and therefore the relative blood flow to the different regions of the myocardium. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a medical imaging technique that is based on conventional nuclear medicine imaging and tomographic reconstruction methods. The images reflect functional information about patients similar to that obtained with positron emission tomography (PET). A Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) scan is a type of nuclear imaging test that shows how blood flows to tissues and organs. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Figure 1. A SPECT scan of a patient with uncontrolled mplex partial seizures. The temporal lobe on the left emission computed tomography scan (SPECT) and functional MRI. We decided to perform a systematic review of brain SPECT and fMRI in SLE patients with cognitive Singlephoton emission computed tomography ( SPECT, or less commonly, SPET ) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, scintigraphy ). Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a Singlephoton emission computed tomography, frkortad SPECT, r en apparat som ger tredimensionella medicinska bilder av olika funktioner i kroppen. Den anvnds vid medicinsk diagnostik. Den anvnder sig av en eller flera gammakamerahuvuden fr att registrera gammastrlning frn en injicerad radionuklid i patienten. Meckel's scan is a common procedure performed in nuclear medicine. Singlephoton emission computed tomographycomputed tomography (SPECTCT) in a suspected case of heterotopic location of gastric mucosa can increase the accuracy of its anatomic localization. version of single photon emission tomography (SPECT) the blank scan should be inspected to ensure that. Single photonemission computed tomography. A single photonemission computed tomography (SPECT) scan is done in a hospital nuclear medicine department or at a special radiology center by a radiologist or nuclear medicine specialist and a technologist. You will lie on a table that is hooked to a large scanner, cameras, and a computer. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Text Increase: If no seizure occurs during the testing time for the ictal SPECT, the epilepsy patient will be sent to get the interictal SPECT scan. In this case, heshe may need to return to the hospital for a. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography is a functional imaging technique that creates threedimensional images of the brain on computer. This allows physicians to visualize blood flow through different areas of the brain. dopamine transporter imaging with singlephoton emission computed tomography DaTSPECT is based on the selective affinity of dopamine transporter ligands for dopamine synthesizing neurons, which allows visualization of deficits in the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a nuclear medicine technique that uses a rotating camera (single or multiplehead), and a computer to produce images representing slices through the body in different planes. A single photonemission computed tomography (SPECT) scan is done in a hospital nuclear medicine department or at a special radiology center by a radiologist or nuclear medicine specialist and a technologist. You will lie on a table that is hooked to a large scanner, cameras, and a computer. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the added value of single photon emission computed tomographycomputed tomography (SPECTCT) over planar scintigraphy, SPECT and CT alone for characterization of isolated skull lesions in bone scintigraphy (BS) in cancer patients. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Search. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) What is a cardiac SPECT scan? A SPECT scan of the heart is a noninvasive nuclear imaging test. A SPECT scan can be used to examine blood flow in your heart at rest and during exercise (called a nuclear stress test). If you cant.
-
Related Images: