-
Gallery of Images:

-
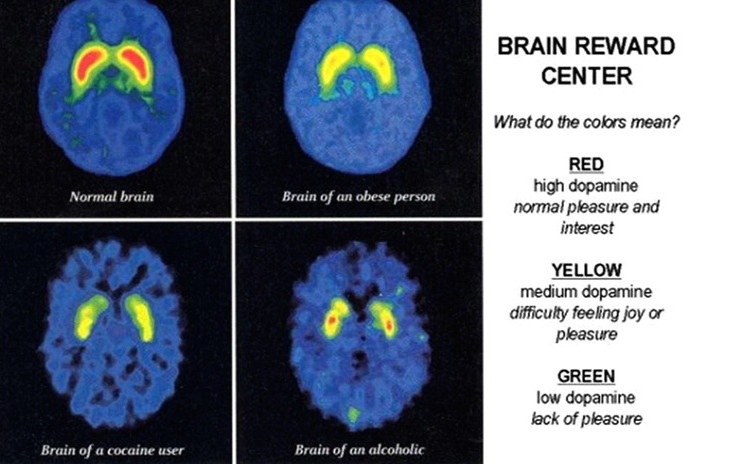
Drugs can affect different areas of the brain including the brain stem which controls the basic functions critical for life, such as breathing and heart rate. Drugs also affect the cerebral cortex which is divided into areas that work to control different functions. The way the brain responds to repeated substance abuse plays a big part in drug and alcohol addictions. The abuse of addictive substances activates the brain's reward system. Frequently activating this system with drugs can lead to addiction. Learn how changes within the brain can affect your addiction. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Common neurobiological elements are emphasized that provide novel insights into how the brain mediates the acute rewarding effects of drugs of abuse and how it changes during the transition from. About this course: The neuroscience of drugs for therapy, for prevention, and for recreation. Youll learn the prospects for new generations of medications in neurology, psychiatry, aging, and treatment of substance abuse. Addiction is a disease that affects your brain and behavior. When youre addicted to drugs, you cant resist the urge to use them, no matter how much harm the drugs may cause. Addiction is a chronic brain disease that's more about the neurology of the brain than the outward manifestations of behavioral problems and poor choices, according to a. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Common neurobiological elements are emphasized that provide novel insights into how the brain mediates the acute rewarding effects of drugs of abuse and how it changes during the transition from. For many years, experts believed that only alcohol and powerful drugs could cause addiction. Neuroimaging technologies and more recent research, however, have shown that certain pleasurable activities, such as gambling, shopping, and sex, can also coopt the brain. All addictive drugs affect brain pathways involving rewardthat is, the dopamine system in the reward pathway. Within seconds to minutes of entering the body. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Heroin addiction is a treatable condition, but its use is increasing in recent years. According to the 2011 Survey on Drug Use and Health by the US Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration, it is estimated that 607, 000 persons per year used heroin in the years, compared to 374, 000 during. Drugs can alter important brain areas that are necessary for lifesustaining functions and can drive the compulsive drug use that marks addiction. Brain areas affected by drug use include. One of the side effects of drug and alcohol abuse that is not well known is brain damage and injury. Most publicized is the potential for acute damage due to overdose or even damage to other organs in the body, such as liver damage from alcohol abuse or heart damage from use of stimulants. When the brain gets too much dopamine from drugs, it learns to continue to search for that high in favor of the lesser pleasure that it would normally get from other, daily rewards, such as. Sanjay Gupta says the brain is rewired when someone becomes addicted. While you may begin using drugs voluntarily, eventually the drugs alter your brain function. This impairs your ability to feel normal or to think clearly and rationally without drugs. All of this contributes to the compulsive drug use and drugseeking behaviors that are common with teen drug addiction. drugrehab Addiction, Addiction Genetics, Friends and Family of Addicts, Side Effects of Substance Abuse. If addiction is a disease of the brain, what exactly does that mean? It is easy to comprehend what a disease is. For instance, asthma is a disease that affects the respiratory system. The Addicted Brain from Emory University. This is a course about addiction to drugs and other behaviors. It will describe what happens in the brain and how this information helps us deal with and overcome addiction. For many years, experts believed that only alcohol and powerful drugs could cause addiction. Neuroimaging technologies and more recent research, however, have shown that certain pleasurable activities, such as gambling, shopping, and sex, can also coopt the brain. This is because addiction caused the brain's balance to change to accommodate the addiction. Once changed, the brain requires the addictive substance or activity in order to. Bowling Green Rehab Addiction Brain; Methamphetamines Prescription Drugs Rehab Facilities In Ri Addiction is a chronic brain disease that often happens again. It causes compulsive drug seeking and use despite harmful effects on the addicted person and the people around that person. Most PET studies of drug addiction have concentrated on the brain dopamine (DA) system, since this is considered to be the neurotransmitter system through which most drugs of abuse exert their reinforcing effects. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Common neurobiological elements are emphasized that provide novel insights into how the brain mediates the acute rewarding effects of drugs of abuse and how it changes during the transition from. Addiction is a brain disorder characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli despite adverse consequences. Despite the involvement of a number of psychosocial factors, a biological process one which is induced by repeated exposure to an addictive stimulus is the core pathology that drives the development and maintenance of an addiction. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Common neurobiological elements are emphasized that provide novel insights into how the brain mediates the acute rewarding effects of drugs of abuse and how it changes during the transition from. 3 This explains why addicts lose interest in things, activities and people they once loved during the slide into addiction. If the brain encounters drug or alcoholinduced overstimulation occasionally, it responds defensively to each as. Watch videoAddiction comes in many forms trapping millions across the globe in a vicious cycle of desire, bingeing, and withdrawal. With the latest research on how the brain works, scientists are challenging the notion that addiction represents some kind of moral failing. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Addiction is now understood to be a brain disease because scientific research has shown that alcohol and other drugs can change brain structure and function. Advances in brain imaging science make it possible to see inside the brain of an addicted person and pinpoint the parts of the brain affected by drugs of abuse providing knowledge that. While each drug produces different physical effects, all abused substances share one thing in common: repeated use can alter the way the brain functions. This includes commonly abused prescription medications as well as recreational drugs. Its clear that the brain is the central control for addiction, and drugs create that addiction when they are inserted into the complex messaging system. The most damage, in terms of addiction, is done in the reward system of the brain. Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is an adaptive state that develops from repeated drug administration, and which results in withdrawal upon cessation of drug use. [1 [2 A drug addiction, a distinct concept from substance dependence, is defined as compulsive, outofcontrol drug use, despite negative consequences. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Common neurobiological elements are emphasized that provide novel insights into how the brain mediates the acute rewarding effects of drugs of abuse and how it changes during the transition from initial drug use to compulsive drug use and addiction. If you think drugs won't affect your health, think again. Get the facts about the most commonly abused drugs. Learn what they are and how using drugs, even just once, can affect your body and your mind. The notion that drug addiction is a brain disease has become axiomatic. Around the globe aspiring health professionals treating substance abuse are indoctrinated with this belief, especially after the idea became popular in the 1990s. Drug addiction is a complex and chronic brain disease. People who have a drug addiction experience compulsive, sometimes uncontrollable, craving for their drug of choice. Typically, they will continue to seek and use drugs in spite of experiencing extremely negative consequences as a result of using. The more often drugs are used, the more they will impact brain chemicals and circuitry, which can lead to drug dependence and withdrawal symptoms when the drugs process out of the body. Drug cravings, dependence, and withdrawal symptoms, coupled with a loss of control over use, are signs of addiction. The majority of drugs have a direct or indirect effect on the neurons in the brain, specifically on neurotransmitters and receptors at the synapse. Drugs can cause disruption in the brains normal Drugs Hijack Communication in the Brain. The brain is a finely tuned machine, and individuals who abuse drugs upset its delicate balance. These outside chemicals can flood or supplant the brains natural circuitry, resulting in effects ranging from confusion to death. The Science of Addiction Image: White Matter Fibers, Parietal Areas III. Drugs and the Brain the hallmark of addiction. Brain imaging studies of people with addiction show physical changes in areas of the brain that are critical to judgment, decision making, learning and memory. Shortcomings of the Neurocentric View of Addiction. For all its benign aspirations, there are numerous problems with the braindisease model. On its face, it implies that the brain is the most important and useful level of analysis for understanding and treating addiction. How Science Has Revolutionized the Understanding of Drug Addiction For much of the past century, scientists studying drugs and drug use labored in the shadows of powerful myths and misconceptions about the nature of addiction. The majority of drugs have a direct or indirect effect on the neurons in the brain, specifically on neurotransmitters and receptors at the synapse. Drugs can cause disruption in the brains normal To understand how addiction forms, you first have you understand the effects of drugs on the brain. There are three main categories of drugs that interact with the dopamine system: Stimulants like cocaine and ecstasy directly affect dopamine transmitters. Drug Addiction Brain: Drug Rehab# [ Drug Addiction Brain# Find Out How You Can Start Rehab Today! Drug Addiction Brain What Drug Addiction; Arizona Drug Rehab Centers Recovery Drugs And Alcohol; Christian Alcohol Rehab Programs St Vincent De Paul Owensboro Ky; Drug Rehab In South Carolina; Drug Addiction Brain. Drugs, Addiction, and the Brain explores the molecular, cellular, and neurocircuitry systems in the brain that are responsible for drug addiction. Common neurobiological elements are emphasized that provide novel insights into how the brain mediates the acute rewarding effects of drugs of abuse and how it changes during the transition from. But maybe it is not that simple. This video is adapted from Johann Hari's New York Times bestselling book 'Chasing The Scream: The. Addiction is a chronic brain disease that causes a person to compulsively seek out drugs, despite the harm they cause. The first time a person uses drugs, its usually a free choice theyve made. Drugs Teen Brain Development Your teens brain is growing by leaps and bounds during these formative years, and is especially sensitive to outside influences such as substance use. When children abuse drugs or alcohol, their brain development is stunted, sometimes irreversibly..
-
Related Images: