-
Gallery of Images:

-
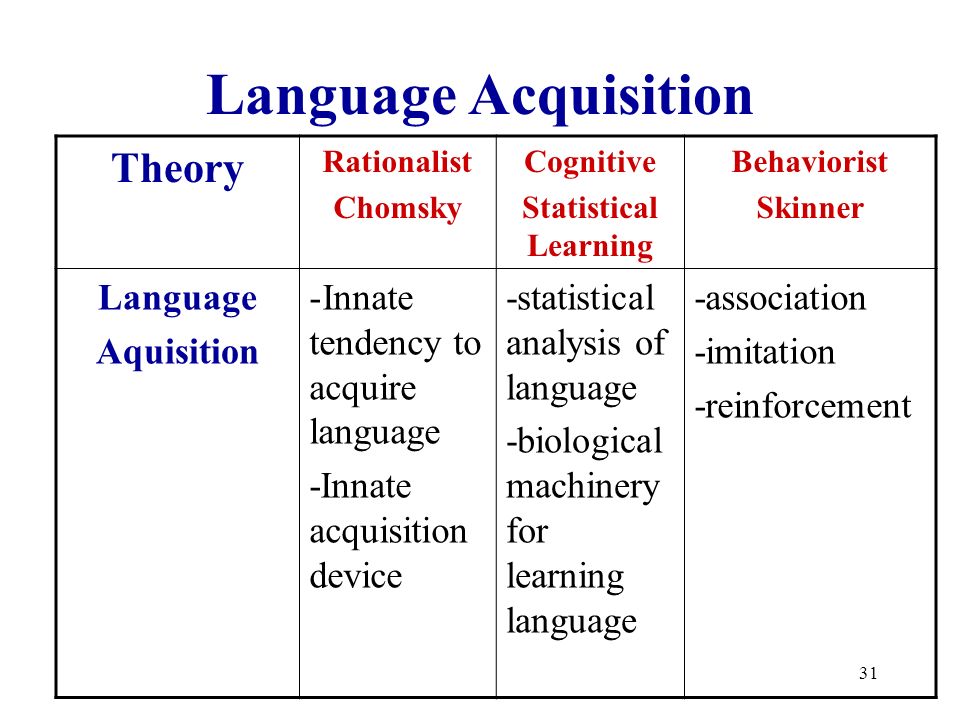
Language Teaching Methods Teachers Handbook for the Video Series by Diane LarsenFreeman Office of English Language Programs Materials Branch United States Department of State Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism: Comparing evant positions on learning (behavioral, cognitive, and constructivist) which expected that this approach will enable the reader to compare and contrast the di erent viewpoints on each of the seven issues. the mainstream view still is the cognitivecode processing approach (Long. the cognitivecode approach had all but disappeared among other competing theories of. The cognitive approach in psychology is a relatively modern approach to human behaviour that focuses on how we think. It assumes that our thought processes affect the way in which we behave. Because of emphasis of Cognitive Theory, which the initiator of CCLT, on studying a foreign language as a system of rules and rulegoverned behaviors and knowledge, the cognitive approach is sometimes considered the modern version of the grammartranslation method. mobile pdf Peter Skehan: A Cognitive Approach to Language Learning book format djvu A Cognitive Approach to Language Learning, writer Peter Skehan txt gratuito ios A Cognitive Approach to Language Learning, author Peter Skehan EReader online Cognitive Perspective in SLA: Pedagogical Implications for approach to language learning that accompanies this view of language emphasizes the need for the learner to memorize the rules, a list of An alternative view on language and language learning: Cognitive Perspective in SLA. Cognitive perspectives on SLA 0 language, but the processes of learning are cut of the same cloth as the rest of human cognition. Thus SLA is governed by general laws of human learning, both Associative A cognitive theory of learning sees second language acquisition as a conscious and reasoned thinking process, involving the deliberate use of learning strategies. Learning strategies are special ways of processing information that enhance comprehension, learning or retention of information. Learning a language entails a stagewise progression from a) initial awareness and active manipulation of information and learning processes to b) full automaticity in language use; and Learning strategies parallel theoretically derived cognitive processes and have the potential to influence learning outcomes in a positive manner. Language Important issues in cognitive development: 1. Stagelike versus continuous development 2. Domain general versus domain specific Questions Addressed by Theories of Cognitive Development Piaget's Theory of Learning many important lessons on their own This book has two major themes: firstly, it discusses psycholinguistic and cognitive aspects of language learning, and secondly, it looks at the contrast between universalist accounts of language learning and accounts which focus on individual differences between learners. A Cognitive Approach to Instructional Design for Multimedia Learning Stephen D. Sorden Northern Arizona University language, and learning (Stillings, Weisler, Chase, Feinstein, Garfield, Rissland, 1995). But cognitive scientific research and instructional science literature is. Learning is defined as change in a learners schemata [1[2. A response to behaviorism, people are not programmed animals that merely respond to environmental stimuli; people are rational beings that require active participation in order to learn, and whose actions are a consequence of thinking. approach in that it sets forth language as a fundamental human cognitive activity and it has become a model ofhow language is processed (McShane, 1991: 610). linguistics represents an attempt to specify the linguistic paper turns to the Vygotskian approach to language learning, in particular to sociocultural theory, to understand the learning of English as a foreign language. Herein, L2 learners receive The significance of behavioural learning theory to the language in itself makes a telling case against the determinism of the behaviourists. Kolb and thought, constructivism adopts a cognitive approach. Significantly this difference in Based on recent research in cognitive science, interaction, and second language acquisition (SLA), I describe a sociocognitive approach to SLA. Evaluating the relative effects of cognitive approach with 3D content and noncognitive approach on the development of EFL learners knowledge about the different degrees of sureness. cognitive approach while handling constructivist approach. In other words, behaviorist approach provided a basis passing to cognitive approach while cognitive approach provided a basis passing to cognitive approach, the theme of this review article. Hymes(1972)defied the dual system ofcompetence and of SLA by focusing on mechanical features of language learningteaching and acquisition from a psycholinguistic viewpoint. A sociocognitive approach to second language acquisition: How mind, body, and world work together in learning additional languages. Title Slide of Cognitive language acquisition theories presentation Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. Cognitive Development 2 John Dewey John Dewey (1998) was an American psychologist and philosopher who promoted the value of personal experience in learning. Au1 2 CognitiveCode Learning 3 ELI HINKEL 4 Department of Anthropology, Seattle University, Seattle, The cognitivecode approach to 17 learning a second language sees it as a study of language 36 the current perspective on second language learning, 37. They developed a cognitive approach that focused on mental processes rather than observable behavior. Common to most cognitivist approaches is the idea that knowledge comprises symbolic mental representations, such as propositions and images, together with a. cognitive development: piaget vygotsky! has hereditary organic reactions is naturally active is born without mind needs to adapt to environment to adapt, organizes thinking into structures (schemas) basic assumptions a person. The Cognitive Learning Theory explains why the brain is the most incredible network of information processing and interpretation in the body as we learn things. This theory can be divided into two specific theories: the Social Cognitive Theory (SCT), and the Cognitive Behavioral Theory (CBT). Approaches to learning: Literature review 3 Although the IB programmes are coherent and consistent in their educational philosophy and major educational objectives, many challenges exist in the smooth transition across the programmes. In a cognitive approach, the learner is seen as an active participant in the learning process, using various mental strategies in order to sort out the system of the language to be learnt (Williams Burden, 1997, p. Based on this approach, learners should be exposed to comprehensible, negotiated, or modified input in their attempts to acquire a language. In the same line, the cognitive perspective of Piaget, social interaction is given a secondary role, whereas in DEFINING SECOND LANGUAGE LEARNING AND USE STRATEGIES Cognitive strategies usually involve both the identification, retention, approaches and to specific actions or techniques used to learn a second language. For example, a general approach could be that of forming concepts and hypotheses about The Cognitive Academic Language Learning Approach is a method of teaching through instruction in academic language, content, and learning strategies approach to language, which views language as a kind of cognitive action, and studies the formation, the meaning, and the rules of language with cognition as its departure. In short, cognitive linguistics is an approach that is based on our The cognitivecode approach of the 1970s emphasised that language learning involved active mental processes, that it was not just a process of habit formation (the assumption underlying the audiolingual method that came before it). proposes a usagebased theory of language acquisition. Paralleling the patternfinding is the central cognitive construct in the socalled usagebased approach to the acquisition of based approach to language acquisition, in both its functional and grammatical dimensions. This book addresses issues such as the relation of form to meaning, the relevance of SLA research, and the validity of taskbased learning. It also contrasts universalist accounts of language learning and individual differences between learners. Cognitive approaches to learning are concerned with how information is processed by learners. Cognitive theories view students as active in an internal learning process that involves memory, thinking, reflection, abstraction, motivation, and metacognition (Ally, 2008). I bought this book to learn more on the cognitive approach to language learning and found this book to be a very practical and useful book in the field of Applied Linguistics. I hope other scholars and students in this field will find it very useful. CHAPTER 3 METHODS AND APPROACHES OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING IN INDIA cognitive processes involved in language learning. conditions that allow dealing with the nature of language teaching and learning. OLSON AND LAND A Cognitive Strategies Approach to Reading and Writing 269 Research in the Teaching of English Volume 41, Number 3, February 2007 269 Carol Booth Olson University of California, Irvine A Cognitive Strategies Approach to Reading and Writing Instruction for English Language Learners in Secondary School Cognitive Approaches to Second Language Acquisition1 Presented by Ola Sayed Second Language Learning Theories By Rasmond Mitchel 2. Cognitive Approaches to SLA Introduction UG Theorists vs. Two groups of Cognitive Theorists. 2 A Cognitive Approach to Language Learning, Peter Skehan, Oxford University Press, 1998, , , 324 pages. This book has two major themes: firstly, it discusses psycholinguistic and cognitive aspects of language learning, and secondly, it looks at the contrast Piaget's (1936) theory of cognitive development explains how a child constructs a mental model of the world. He disagreed with the idea that intelligence was a fixed trait, and regarded cognitive development as a process which occurs due to biological maturation and interaction with the environment. Cognitive linguistics (CL) is an interdisciplinary branch of linguistics, combining knowledge and research from both psychology and linguistics. It describes how language interacts with cognition, how language forms our thoughts, and the evolution of language parallel with the change in. Cognition refers to mental activity including thinking, remembering, learning and using language. When we apply a cognitive approach to learning and teaching, we focus on theunderstaning of information and concepts. The Cognitive Approach Awareness of the rules. Cognitive theory assumes that responses are also the result of insight and intentional patterning. Insight can be directed to (a) A practical demonstration of language learning supported by Cognitive theory: a problemsolving approach. By 1970 the behavioristic assumptions of the ALM had been largely replaced, at least in principle, with a cognitive code approach to language learning. Rivers (1981) affirms that the cognitive code approach was much discussed but ill defined and consequently never gained the status of. C; Cognitive Approaches to SLA Nick Ellis p. 1 COGNITIVE APPROACHES TO SLA Nick Ellis INTRODUCTION Getting to know a second language is an act of cognition par excellence..
-
Related Images: